TATA MEDICAL CENTER
Cancer Awareness
CANCER………………….The Epidemic of Today
Cancer is a deadly disease and is struggling hard presently to become the number one killer of our times .The incidence of cancer is increasing. This is because of increasing longevity, changing lifestyle, increasing pollution and many other factors. Three out of every ten people in the world will have cancer in their lives by 2025 .Cancer is increasing in India too and in the next 15 years or so, one out of every six person, will have cancer, which means that at least one member of every family will have a patient suffering from cancer. It is hence imperative that we all know the basics about cancer and its causes, early symptoms and methods of treatment. The study of Cancer is called Oncology,
The most common cancers in the world are of Lung, prostrate, colon (large gut), and rectum. In India the three most common cancers in women are of cervix, breast and esophagus (food pipe) and in men, the head and neck region and esophagus are affected by cancer most commonly. Over one third of all the cancers of the head and neck region, of the world affect Indians
What is Cancer?
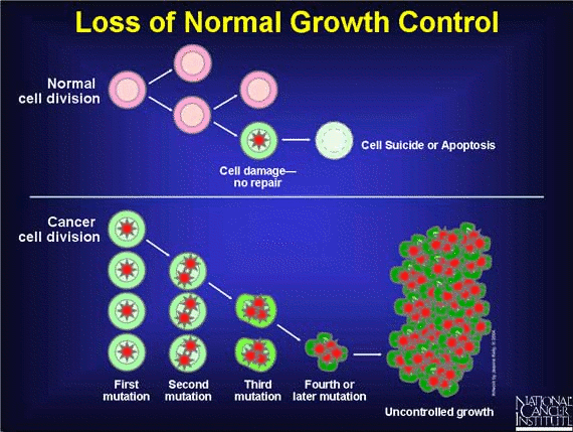 Cancer is a purposeless growth of cells, which is unresponsive to the normal growth control mechanism of the body. These soon become so large that they cause adverse impact on the body. This is done by various methods
Cancer is a purposeless growth of cells, which is unresponsive to the normal growth control mechanism of the body. These soon become so large that they cause adverse impact on the body. This is done by various methods
- Cancer cells use up body nutrients and deprive the normal cells of food and energy
- If on surface they can cause disfigurement and ulceration
- By fast growth they cause pain
- They may obstruct blood vessels, intestine, airway, food pipe etc
- They secrete hormone like substances which cause fever, weakness and other metabolic imbalance
- It may spread to distant organs and cause organ failure
Benign or Malignant
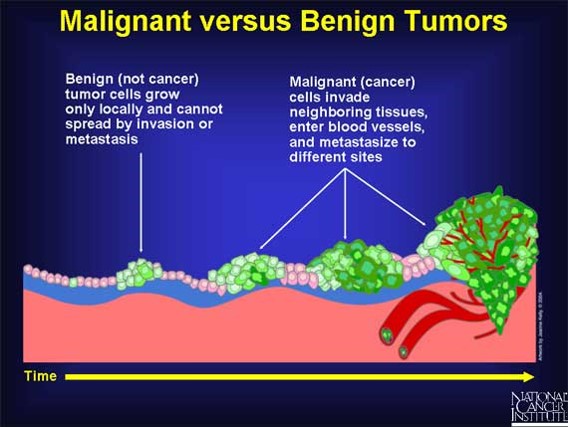 Cancer is often confused with tumor. Neoplasia, which is a purposeless growth of cells, can be of two types, Benign or Malignant. The benign one is the harmless growth and is normally called a tumor, these are slow growing, normally well localized in a capsule and almost never spread to distant organs. Very few tumors may invade local tissue or organs. Malignant neoplasm is the harmful one, which is called Cancer. This is fast growing, does not have a localizing capsule, infiltrates into local tissue and spreads to distant organs, often leading to death. Spread of cancer to distant organs is called metastasis. The common organs affected by metastasis are lymph nodes, liver, lung, bones and brain.
Cancer is often confused with tumor. Neoplasia, which is a purposeless growth of cells, can be of two types, Benign or Malignant. The benign one is the harmless growth and is normally called a tumor, these are slow growing, normally well localized in a capsule and almost never spread to distant organs. Very few tumors may invade local tissue or organs. Malignant neoplasm is the harmful one, which is called Cancer. This is fast growing, does not have a localizing capsule, infiltrates into local tissue and spreads to distant organs, often leading to death. Spread of cancer to distant organs is called metastasis. The common organs affected by metastasis are lymph nodes, liver, lung, bones and brain.
Types or Cancers
Cancers are of various types depending upon the organ or part of the body involved. The common ones are
- Adenocarcinomas ,Squamous Cell Carcinomas ,Transitional Cell carcinoma- these affect the common organs of the body.
- Sarcoma-these are cancers of connective tissue like muscles, bone, fat etc
- Lymphomas and Leukemia- this affects the nodes and the blood cells
Causes of Cancer
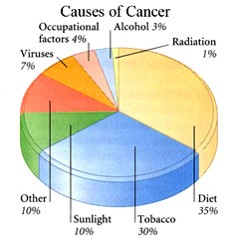 The exact cause of cancer is not known. but it is believed that changes(mutations) in the genes lead to cancer. These changes may be caused by various factors like genetics, hereditary, geographical distribution, chemicals like aniline, benzene etc, chronic friction like old injury or burn scar, exposure to ionizing radiations and ultraviolet rays, smoking, drinking, use of pan, pan masala and tobacco, poor hygiene and certain preexisting diseases or conditions.
The exact cause of cancer is not known. but it is believed that changes(mutations) in the genes lead to cancer. These changes may be caused by various factors like genetics, hereditary, geographical distribution, chemicals like aniline, benzene etc, chronic friction like old injury or burn scar, exposure to ionizing radiations and ultraviolet rays, smoking, drinking, use of pan, pan masala and tobacco, poor hygiene and certain preexisting diseases or conditions.
Myths and Facts About Cancer
- Age:- Cancer is not the disease of old age only, it can occur in any age and at times .Even a baby can be born with cancer.
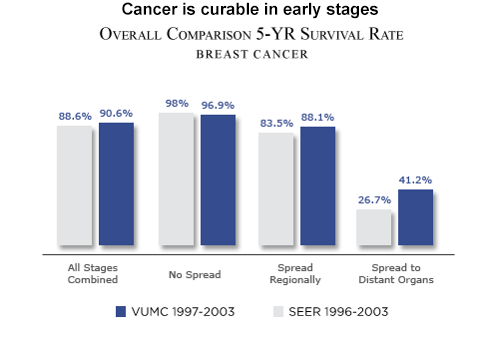
- Survival and Cure Diagnosis of Cancer does not mean a death warrant. Cancer can be cured if detected early and a large number of patients survive several years and at times even normal life after having cancer
- Spread:- Cancer is not contagious, It does not spread by staying in the same house or by touch .
- Use of Knife:- People feel that use of knife for biopsy or surgery can spread cancer, but it is not so. Biopsy is essential to diagnose most cancers and plan treatment and surgery where ever possible is the most effective method of treatment in majority of cancers. It removes or decreases the diseased part and makes chemotherapy and radiotherapy more effective
Early signs of Cancer:-
Early detection of cancer is the most important way of curing it. So we must all be very careful of early signs of Cancer. They can be summarized as follows:
- C hange in bowel or bladder habits
- A sore that does not heal
- U nusual bleeding or discharge
- T hickening or lump in breast or elsewhere
- I ndigestion or difficulty in swallowing
- O bvious change in an existing wart or mole
- N agging cough or hoarseness of voice
Besides the above Cancer warning signals, one should consult a doctor in the eventuality of unexplained weight loss, continuous prolonged fever, or general weakness. Patients with family history of cancer or those who have had cancer in the past ,or who have had exposure to radiation or are working in an industry where they are in contact with chemicals are at high risk for cancer and should be careful, and undergo periodic checkups
The routine checkups advised in our country for common cancers is as follows
Woman
- Cancer of Cervix – PAP Smear Test every 2-5 years from the age of 35
- Cancer Breast -Mammography every 5 years from the age of 35 years
- Self Breast Examination every month
- Breast examination by the doctor every 2-5 years
Men
- Prostate – PSA (Prostatic Specific Antigen ) every 5 years from the age of 45years
- Colon and Rectum -Stool for occult blood and per rectal examination every 2-5 years from the age of 45 years
Prevetion of Cancer
Avoid tobacco,smoking and alcohol consumption
Eat balanced Diet full of green vegetables and fresh fruit
Avoid Obesity
Diagnosis of Cancer
The Diagnosis of Cancer involves three sets of investigations
Confirmation of Diagnosis, by biopsy
- Cytology
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology or Biopsy (FNA/FNAB)
- Cytology of Fluids
- Histopathology
- Endoscopic Biopsy
- Stereostatic Biopsy
Staging workup, to see the extent of disease locally, its spread and the operability
General Investigations, to assess the general fitness of the patient to undertake the treatment
Routine investigations done for diagnosis and staging of cancer are – X Rays, Ultrasound, Endoscopy, Doppler, CT Scan (Computerized Axial Tomography), MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), Radioactive Scans, Tumor Markers(CA-125, PSA, CEA, AFP, BHCG, Calcitonin, Thyroglobulin)
The various modality of treatment of cancer are as follows:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Hormonal therapy
- Miscellaneous therapies like laser, radioactive ablation, gamma knife etc.
Myths and Facts About Cancer
Though cancer has existed since very long, its detailed knowledge is just over a century old in the history of medicine. And in spite of its significant prevalence and adequate efforts to spread cancer awareness amongst the common man, by all concerned, there are still a large number of myths existing, regarding cancer even in the mind of educated people.
- Age – Cancer is not the disease of old age only, it can occur in any age and at times .Even a baby can be born with cancer.
- Survival and Cure – Diagnosis of Cancer does not mean a death warrant. Cancer can be cured if detected early and a large number of patients survive several years and at times even normal life after having cancer
- Spread – Cancer is not contagious, It does not spread by staying in the same house or by touch .
- Use of Knife – People feel that use of knife for biopsy or surgery can spread cancer, but it is not so. Biopsy is essential to diagnose most cancers and plan treatment and surgery where ever possible is the most effective method of treatment in majority of cancers. It removes or decreases the diseased part and makes chemotherapy and radiotherapy more effective
Early signs of Cancer
Early detection of cancer is the most important way of curing it. So we must all be v
ery careful of early signs of Cancer. They can be summarized as follows
- C hange in bowel or bladder habits
- A sore that does not heal
- U nusual bleeding or discharge
- T hickening or lump in breast or elsewhere
- I ndigestion or difficulty in swallowing
- Obvious change in an existing wart or mole
- N agging cough or hoarseness of voice
Besides the above Cancer warning signals, one should consult a doctor in the eventuality of unexplained weight loss, continuous prolonged fever, or general weakness. Patients with family history of cancer or those who have had cancer in the past ,or who have had exposure to radiation or are working in an industry where they are in contact with chemicals are at high risk for cancer and should be careful, and undergo periodic checkups
The routine checkups advised in our country for common cancers is as follows
Woman
- Cancer of Cervix – PAP Smear Test every 2-5 years from the age of 35
- Cancer Breast -Mammography every 5 years from the age of 35 years
- Self Breast Examination every month
- Breast examination by the doctor every 2-5 years
Men
- Prostate – PSA (Prostatic Specific Antigen ) every 5 years from the age of 45years
- Colon and Rectum -Stool for occult blood and per rectal examination every 2-5 years from the age of 45 years
Stages of Cancer –The first question that every patient or the relative ask after diagnosis of cancer is that what is the stage of cancer? Though all cancers have their specific staging systems, there are following four broad stages. Stages 1 and 2 have very good chances of cure, but unluckily more than half of the patients in our country report for treatment in stage three and four due to lack of facilities and ignorance.
Stage 1 The cancer is restricted to the organ or site of origin
Stage 2 The cancer has spread locally outside the organ or site of origin
Stage 3 The Cancer has spread to the nodes
Stage 4 The Cancer has spread to distant organs (Metastatic Cancer)
Diagnosis of Cancer
Proper diagnosis of cancer is essential for starting correct treatment, and diagnosis can be achieved by various methods. The two common methods are Cytology and Histopathology
- Cytology:- Here the diagnosis is made by seeing cancer cells in the material sent for testing
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology or Biopsy (FNA/FNAB):- Here cells are aspirated from the tumor or cancerous lump by a thin (FNAB) needle and seen under a microscope, This is a very simple test, done without anesthesia or hospitalization and has significantly high accuracy. This is generally done for growths which are under the skin, specially cancer of the breast, thyroid, liver etc. FNAC on cancers of deeper or small organs can be done under guidance of ultrasound or CT Scan
- Cytology of Fluids:- In certain cases cancer can also be diagnosed on finding cancer cells in fluids collected in the body cavity, like the abdomen or thorax or in urine
- Histopathology:- This is the best method of diagnosis. Here a biopsy is taken from the cancerous part for diagnosis. A node, complete growth or a part of it can be removed and biopised
- Endoscopic Biopsy:- Biopsy of the foodpipe, stomach and intestines is done by endoscopy and colonoscopy and of the airway by bronchoscopy
Stereostatic Biopsy – Biopsy of small lesions or lesions in structures like brain are done after being localalised by fine needles under CTSan guidance
FACTS ABOUT CANCER
1 Cancer can occur at any age
2 Cancer can be cured, if detected early
3 FNAC, Biopsy or surgery does not increase the spread of cancer
4 Cancer is treated with surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, with most patients getting two or three of these modalities
5 Cancer is not contagious and does not spread by contact or by staying together
6 Cancer patients can lead normal active life after and even during treatment
7 Cancer treatments is prolonged, generally spreading over 6-8 months or more
8 Cancer patients, besides treatment need a lot of support from all, especially families
ADD LIFE TO DAYS AND NOT DAYS TO LIFE
TOGETHER WE SHALL CONQUER
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PATIENTS ON CHEMOTHERAPY
1 Chemotherapy is given to most of cancer patients
2 It is given in cycles, usually of three weeks each, over 4-5 months
3 Patients on chemotherapy should get their blood tests done, a day before chemotherapy
4 Chemotherapy may cause vomiting and nausea
5 Patients should drink adequate water during and soon after chemotherapy
6 Patients should avoid eating heavy meals, oily food and raw fruits and vegetables
7 Patients should take the medicine prescribed after chemotherapy for five days, without fail
8 In case of high fever, or severe vomiting and loose motions after chemotherapy, patient should report to the medical oncologist
9 Patients should avoid going to congested areas and in crowds during chemotherapy
10 Patients may develop blackening of skin and nails, loss of hair, and ladies may stop having periods, but all this may be temporary
Diagnosis of Cancer
The Diagnosis of Cancer involves three sets of investigations
Confirmation of Diagnosis, by biopsy which we discussed in the last issue
Staging workup, to see the extent of disease locally, its spread and the operability
General Investigations, to assess the general fitness of the patient to undertake the treatment
The routine investigations to asses the general fitness of the patient include blood tests for hemoglobin, white cell count, sugar, liver function tests, kidney function tests, proteins and electrolyte(to detect nutritional deficiencies) and blood grouping
X Rays
X-ray chest to see the state of the lungs and any spread to the lungs
X-rays of the limbs, head, spine are done when cancers of the bone are suspected, or in cancers of muscles, to see the involvement of bones
Ultrasound
Ultrasound of the Abdomen -This is a simple OPD procedure, which is cheap, painless, fast and very informative. Besides giving details of the cancers of the abdominal organs (digestive system, kidneys, liver, gall bladder and female organs like uterus, ovary etc) it is helpful in showing the spread to the liver and the nodes.
Ultrasound of the neck is done to see the nodes in the neck and for glands like the thyroid
Ultrasound of the breast and other swellings on the limbs are done too to see if the swelling contains water or is solid
Scopy
Scopy is an investigation where the inside of a hollow organ is seen by an instrument which has fiber optic light. It not only shows the cancer or the disease but also can be used to take a biopsy, stop bleeding, and put stents to bypass blocks and perform other procedures
Usually done without anesthesia
Upper Gastrointestinal Scopy
This is for the stomach and the upper intestines. This is done through the mouth and can also be used to see the pancreatic duct and the bile duct. ERCP(Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatico graphy) is done by this too
Broncoscopy is done through the nose to see the air passage and the lungs
Nasopharyngoscopy is done to see the inside of the nose, through the nose
Laryngoscopy is done to see the Larynx (Voice Box) through the nose
Colonoscopy is done through the rectum to see the large intestines
Doppler
Doppler is done over blood vessels (artery and veins) to see the blood flow in them, and to find the involvement of the vessels or any compression on them by the tumor. This is like the ultrasound and done externally
Computerized Axial Tomography
Commonly called CAT scan or CT scan, this is a very common investigation done to see the extent of the cancer. It gives a very good picture of the cancer, the organs involved, and the local and distant spread. It is however a little expensive and not available in all the hospitals in our country. It is very helpful in cancers of the chest, abdomen and brain and is a great help in deciding the extent of surgery and the treatment for the patient
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Like Tuscan, MRI is a very helpful investigation to see the internal organs, specially the bones, spine, limbs and the head
Radioactive Scans
These are done by injecting radioactive dyes specific for particular organ and subsequently picking up the radio sensitivity by special cameras. They help to see the involvement of various organs and the functioning. Commonly done scans are for bone, liver, kidney and thyroid gland
Tumor Markers
These are tests done on blood. Tumor Markers are substances which are normally not found in the blood or found in very small quantities. The presence or rise of these in the blood is an indicator of cancer. It is very good investigation to see the response to treatment in which situation it will fall to normal and for follow-up of cancer patients, where rise in the levels after treatment indicates relapse. Following are some common tumor markers
CA-125 for cancer of ovary
PSA (Prostates Specific Antigen) for cancer prostate
CEA (Carcinoma Embryonic Antigen) for cancer of large intestines and rectum
AFP (Alpha Fetor Protein) for cancer of testis and liver
BHCG (Beta Human Chronic Gonadotropin) for cancer of testis and ovary
Calcitonin for Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
Thyroglobulin for cancer of thyroid
What is Chemotherapy ?
Chemotherapy is the use of drugs in cancer treatment. Besides surgery and radiotherapy, chemotherapy is one of the three main modalities of treatment in cancer. In the multimodality treatment of cancer, chemotherapy is used in more than three fourths of the patients at some stage or the other. The medical branch dealing with chemotherapy is called Medical Oncology and the oncologist giving chemotherapy is known as Medical Oncologist.
Chemotherapy Drugs
There are about 100 chemotherapy drugs belonging to various groups. The common ones are adriamycin, taxol, cyclophosphamide, cisplatinum, methotrexate, 5 flurouracil. Mitomycin, bleomycin, etoposide etc. They are usually given as intravenous injections in the veins but few drugs can be given orally too.
Indications of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is used in various settings; it can be used as the following:-
- Primary Chemotherapy – where chemotherapy is used as the main mode of treatment as in leukemia, lymphoma and cases which are inoperable or patient is unwilling for surgery
- Preoperative Chemotherapy – here chemotherapy is used before surgery to make the cancer operable or to decrease the extent of surgery and to preserve the affected organ
- Post operative– here chemotherapy is used after surgery to prevent local and distant recurrence
- Salvage – here chemotherapy is used for recurrence
- Palliative– chemotherapy may also be used to decrease pain and other symptoms in advanced cancers
- Chemoprevention– chemotherapy is also used in certain cases to prevent cancer in high risk patients or to prevent second cancer in cancer patients
Duration of Chemotherapy
There are various schedules of chemotherapy. It is usually given in cycles repeated every 3 weeks. Normally a patient receives six cycles. Some drugs are given over few hours while others may be given continuously for two to five day. Some regimes have a weekly schedule of chemotherapy and few drugs specially those being taken orally are given daily.
Actions of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy prevents cell division and leads to cell death. Maximum effect is on the cancer cells, however normal cells are affected too. The most commonly affected normal cells are of the bone marrow, blood and the intestines.
Preparation For Chemotherapy
Before chemotherapy the following blood tests should be done, hemoglobin, blood count, platelet, electrolyte, liver and kidney function tests. If the blood counts are high or low, then chemotherapy should be postponed. Patient should drink a lot of water and have light meals before chemotherapy.
Side Effects of chemotherapy
- Vomiting and nausea
- Loose motions
- Fever
- Low blood counts
- Loss of hair
- Bone marrow suppression
- Stopping of periods
- Blackening of skin and nails
Precautions during chemotherapy
- To drink adequate fluids
- To avoid heavy meals
- To avoid eating raw vegetables or fruits
- To avoid infections
- To avoid going in crowded areas soon after chemotherapy
Ports and catheters
In patients who need chemotherapy for long durations and frequently or in those where veins are not found easily, chemotherapy can be given through special catheters or ports which are placed in a central big vein .The drugs are injected directly into the catheter which are outside the body or the port which are placed under the skin. These prevent frequent injection of drugs in the veins.
Chemotherapy is being used extensively these days in the treatment of cancer patients with good results.
What is Radiotherapy ?
Radiotherapy is use of high energy radiation like X-Ray to kill cancer Cell. In common language it is called heat treatment. Radiotherapy works by damaging the cancer cells, due to which they are unable to multiply.
It is given for a few minutes only, five days a week for an average of five to six weeks .Radiotherapy may damage some healthy cells too and hence cause side effects.
Types of Radiotherapy
Tele Therapy here radiotherapy is given from a distance. This is the most common form of radiotherapy.
Brachy Therapy here the source of radiotherapy is in contact of the body, as used in cancer of the cervix.
Intraluminal Therapy here the source is put inside the narrow hollow organs of the body like the windpipe or the foodpipe.
Interstitial Therapy here the radiotherapy is passed through very fine tubes placed in the body, as in cancer of the muscles and breast.
Cobalt Therapy is the conventional method of radiotherapy. Here the source of rays is Cobalt.
Linear Accelerator is the modern radiotherapy machine which is more effective, is faster and has less side effects.
Indications of Radiotherapy
Adjuvant used postoperatively to prevent local spread.
Primary used as the main modality of treatment as in cancer of cervix, and few cases of head and neck cancers and in some advanced inoperable cancers.
Pre Operative to shrink the tumor to make it operable and to decrease the extent of surgery.
Palliative given to bones and spine in cases of metastasis to the bone, for severe pain and to prevent fractures. It can also be used to stop generalized bleeding from cancers.
Side effects of Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy may cause nausea, vomiting, dryness of mouth, ulcers in mouth and skin, and diarrhea. These are generally temporary effects. it may however cause severe damage to the lungs, heart, nerves and brain if these organs are not protected well.
DOs and DONTs
- See the doctor at least once while on treatment
- No shaving if getting radiotherapy on face Avoid scrubbing or rubbing the area
- Avoid crowds and meeting people as they could give infection
- Report to the doctor immediately even in case of mild fever or bleeding
- Ensure you do not rub off the markings made on the skin to pinpoint the exact place where the radiotherapy is to be directed
Nutrition
Drink lots of fluids
Eat small frequent meals at room temperature
Eat well-cooked soft food
Avoid hot and spicy food
Eat a good nutritious diet rich in calories and proteins
Avoid tea, coffee, alcohol, and tobacco
Drink juices, soups, coconut water fresh lime etc
General Care
Exercise for a few minutes every day
Rest as much as you can
Do not over exert
Wear loose fitting clothes preferably of soft cotton material
Do not use perfumes, scented soaps etc
Sponge the radiated area lightly with lukewarm water and pat it dry.
CONTACT INFORMATION
Call Us: (033) 6605 7222
Write Us: appointment@tmckolkata.com
For Other Queries:
Call Us: (033) 6605 7000
Write Us: info@tmckolkata.com
For Feedback:
Call Us: (033) 6605 7095 | 9330903299
Write us: info@tmckolkata.com or Click on Feedback
For Patients
FOLLOW THE LINKS
Tata Medical Center, Kolkata
14 MAR (E-W), New Town,
Rajarhat, Kolkata 700 160
West Bengal, India.
